Abstract Reasoning & Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests 2025
All products and services featured are independently selected by WikiJob. When you register or purchase through links on this page, we may earn a commission.
- What Is an Abstract Reasoning Test?
- What Is a Diagrammic Reasoning Test?
- Abstract Reasoning Practice Test (25 Questions)
- What to Expect on an Abstract Reasoning Test in January 2025
- Abstract Reasoning Test Simulation (10 questions)
- Abstract Reasoning Question Types
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
- Example of Abstract Reasoning Questions (25 questions)
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Test
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Question Types
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Test (24 Practice Questions)
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Practice Test (24 Questions)
- Abstract & Diagrammatic Reasoning: Tips and Techniques for 2025
- Final Thoughts
What Is an Abstract Reasoning Test?
Abstract reasoning, also known as abstract thinking or abstract reasoning ability, is a cognitive skill that involves the ability to think conceptually, grasp complex ideas, and identify patterns and relationships among seemingly unrelated or abstract concepts.
It is a higher-order thinking skill that goes beyond concrete, factual thinking and relies on the ability to analyze, synthesize, and draw conclusions based on patterns, principles and generalizations.
Abstract reasoning questions are seen to be a good measure of general intelligence, as they test your ability to perceive relationships and then to work out any co-relationships without requiring any knowledge of language or mathematics.
Because of this, they are frequently used during the interview process for graduate jobs, and you should be prepared to face them.
The abstract reasoning questions require you to recognise patterns and similarities between shapes and figures.
Abstract reasoning is the ability to solve problems, identify patterns, and work with logical systems.
As a measure of reasoning, it is independent of educational and cultural background, and can be used to indicate intellectual potential.
These types of questions are very commonly used in graduate and management selection, and are of particular value when the job involves dealing with abstract ideas or concepts. This can apply to many technical jobs.
You will often encounter them where the job you are applying for involves:
- A high degree of problem-solving
- Dealing with complex data or concepts
- Developing strategies or policies
- Performing non-routine tasks where initiative is required
However, as they also provide the best measure of your general intellectual ability and abstract reasoning skills, they are very widely used. You will usually find some questions of this type whichever assessment you are given.
What Is a Diagrammic Reasoning Test?
Diagrammatic reasoning is a type of cognitive process that involves solving problems or making decisions by analyzing and manipulating visual representations or diagrams.
Instead of relying solely on linguistic or numerical information, individuals use diagrams, graphs, charts or other visual aids to understand relationships, patterns and structures.
Diagrammatic reasoning can take many forms, and it is often used in various fields, including mathematics, science, engineering and everyday problem-solving.
The diagrammatic reasoning tests evaluate these diagramatic reasoning skills. Sample diagrammatic reasoning questions can be seen later in this article.
Credit: Psychometric Success
If you want to take further practice abstract reasoning tests and improve your performance, click here.
Prepare for Any Job Assessment Test with JobTestPrep
What to Expect on an Abstract Reasoning Test in January 2025
Abstract reasoning tests are designed to be challenging, to differentiate between candidates and to identify the maximum performance they are capable of. They usually have tight time scales and questions that rapidly increase in difficulty.
This means that you will need to identify more rules to solve the problems and that the complexity of these rules is likely to increase.
Abstract reasoning tests use diagrams, symbols or shapes instead of words or numbers. They involve identifying the underlying logic of a pattern and then determining the solution.
Questions tend to involve the repetition or change of the following:
- Shape
- Size
- Colour
- Pattern
Abstract reasoning questions use symbols arranged in a straight line or a pattern. You are required to identify the missing symbol or the next in the sequence.
You can expect to be given slightly longer time for these questions than for verbal reasoning and numerical reasoning questions. Thirty minutes to complete 20 questions would be typical.
Prepare for Any Job Assessment Test with JobTestPrep
Abstract Reasoning Test Simulation (10 questions)
Try this free Abstract Reasoning Test before reading on:
Choose the image that completes the pattern.
Prepare for Any Job Assessment Test with JobTestPrep
Abstract Reasoning Question Types
While there are many permutations of question types and formats, there are some general concepts which are common; it's useful to familiarise yourself with these.
These will include abstract reasoning puzzles and sequences.
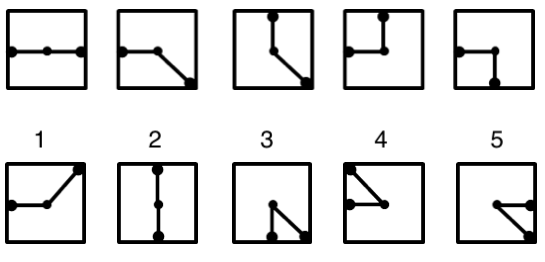
1. Which Figure Completes the Sequence?

Which figure completes the sequence?
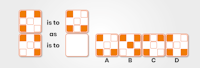
Which figure completes the statement?
Which figure is the odd one out?
Prepare for Any Job Assessment Test with JobTestPrep
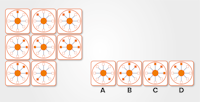
Identify the missing square.
If you need to prepare for a number of different employment tests and want to outsmart the competition, choose a Premium Membership from JobTestPrep.
You will get access to three PrepPacks of your choice, from a database that covers all the major test providers and employers and tailored profession packs.
Prepare for Any Job Assessment Test with JobTestPrep
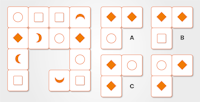
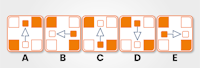
Which figure completes the grid?
Credit: Psychometric Success
Diagrammatic Reasoning Test
Diagrammatic reasoning tests are closely related to abstract reasoning tests, so we've included them here. The questions consist of flowcharts or process diagrams and measure your ability to follow a series of logical instructions or to infer rules presented using symbols.
These types of questions are particularly suited to information technology jobs, because they closely mirror how analysts and programmers approach software design.
Even if you are not applying for an IT-based job, it is worth familiarising yourself with this type of question as they can and do appear in more general abstract reasoning tests, particularly where the job requires analysis of business processes.
Diagrammatic Reasoning Question Types
In the first example, the diagram shows 'inputs' and 'outputs' made up of short 'strings' of letters. The 'operators' or 'processes' are shown in the small boxes.
You need to determine what effect each of the 'operators' or 'processes' is having on the 'input' in order to produce the 'output' shown.
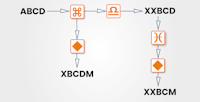
The type of operations or processes you can expect include things like:
- Swapping letters
- Moving letters
- Adding letters
- Removing letters
In this diagram, the black diamond appears twice and must be having the same effect each time.



In the next sample, the operators are defined for you.
The sequence of operations is from top to bottom and each operator acts on the figure that it is attached to. Use this information to answer the questions below.
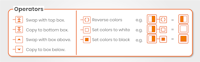

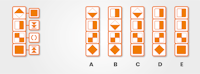
You need to work from top to bottom, making a note of the effect of each operator at each stage. Remember, some of the operations involve changing the relative position of figures.
Subsequent operations may need to be applied to the 'new' figure – not to the one shown.
Credit: Psychometric Success
Credit: Psychometric Success
Abstract & Diagrammatic Reasoning: Tips and Techniques for 2025
Abstract and diagrammatic reasoning ability are closely correlated with general intelligence. However, familiarity with the types of questions you are likely to encounter and some strategies for solving the questions will certainly help you perform at your best.
Here are our five key tips:
-
Many people find that they enjoy the mental challenge of solving abstract reasoning tests. There is a range of puzzle books and apps available that you can use to practise with. Similarly, many test publishers provide practice tests that you can access, such as JobTestPrep; this is certainly worth doing.
-
It can be useful to develop a mental checklist of strategies to solve abstract reasoning questions, such as a list of different rules that govern data like size, shape, number, etc. This gives you a starting point to think about questions and can help you work methodically in the test.
-
Look at one rule at a time. There may be extraneous data within the question which is designed to confuse you. Looking at only one aspect of the question at a time can help you to work out what is important and what isn’t.
-
Manage your time. Sometimes, you will come up against a question where you just cannot see the answer. On these occasions, don’t spend too much time on it, move on and, if you have time at the end, go back and check it. Make a note of any questions you want to come back to. Practise your pacing during your preparation and keep to your ideal pace where possible.
-
If you’re struggling to find a pattern, sometimes there are clues in the answers. Look for any patterns or themes in the possible answers that might help you spot what is important within the question. For example, if you have a sequence of shapes and all of the answers are squares or triangles, you know that the next shape in the sequence must be either a square or a triangle and that can help you work out why.
Remember to listen carefully to the instructions you are given and to read the questions carefully. Sometimes a series of similar-looking questions will be presented but the question may change throughout. Underlining keywords will keep you focused.
Prepare for Any Job Assessment Test with JobTestPrep
Final Thoughts
Abstract reasoning tests are widely used within selection processes to assess a candidate's general intellect and ability to work out new concepts and abstract ideas.
To successfully complete abstract reasoning tests, you need to be able to think creatively and use lateral thinking to solve novel problems. You need to see the relationships between shapes and figures, identify rules and similarities, and quickly apply these to identify the answer.










